Cloud Computing Solutions: Empowering Businesses with Flexibility and Scalability
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline their operations, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. Cloud computing solutions have emerged as a game-changer, offering a wide range of benefits that empower organizations to achieve these goals effectively.
Cloud computing, in simple terms, refers to the delivery of computing services – including storage, processing power, software applications, and databases – over the internet. Unlike traditional on-premises infrastructure, cloud computing eliminates the need for physical servers and hardware installations within an organization’s premises.
One of the key advantages of cloud computing solutions is their inherent flexibility. With cloud-based services, businesses can rapidly scale their resources up or down based on demand. This means that organizations no longer need to invest in expensive hardware or worry about capacity constraints during peak periods. Whether it’s expanding storage capacity or increasing computational power, cloud computing provides the agility required to meet evolving business needs.
Another significant benefit of cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness. By adopting cloud solutions, businesses can avoid hefty upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead, they pay for what they use on a subscription basis. This pay-as-you-go model allows organizations to allocate their resources more efficiently and redirect funds towards critical business areas such as research and development or marketing.
Data security is a top concern for any business operating in the digital age. Cloud computing solutions provide robust security measures that are often superior to those implemented by individual organizations themselves. Cloud service providers employ advanced encryption techniques and implement stringent access controls to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches. Additionally, regular data backups and disaster recovery plans ensure business continuity even in the face of unexpected events.
Collaboration is key to success in today’s interconnected world. Cloud-based solutions enable seamless collaboration among teams regardless of geographical locations. With shared access to files and real-time communication tools, employees can work together efficiently, improving productivity and fostering innovation. Cloud computing also facilitates remote work arrangements, allowing employees to access critical applications and data from anywhere, at any time.
Furthermore, cloud computing solutions offer businesses the opportunity to leverage cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). By harnessing the computational power of the cloud, organizations can process vast amounts of data and gain valuable insights to drive informed decision-making. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming increasingly popular in customer service, enhancing user experiences and reducing response times.
In conclusion, cloud computing solutions have revolutionized the way businesses operate in today’s digital era. With their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, security features, and collaborative capabilities, cloud-based services empower organizations to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace. By embracing cloud computing solutions, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and success.
7 Common Questions Answered: Exploring Cloud Computing Solutions
- What are the benefits of cloud computing solutions?
- How secure is cloud computing?
- What types of cloud computing solutions are available?
- How much does cloud computing cost?
- How do I get started with a cloud computing solution?
- What are the risks associated with using a cloud computing solution?
- Are there any restrictions or limitations to using a cloud computing solution?
What are the benefits of cloud computing solutions?
Cloud computing solutions offer numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing needs without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware or infrastructure.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for large capital expenditures. Businesses only pay for the resources they use, allowing them to allocate their budgets more efficiently and redirect funds towards other critical areas of their operations.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud service providers employ robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches. They implement advanced encryption techniques, access controls, and regular data backups to ensure the security and integrity of sensitive information.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based solutions facilitate seamless collaboration among teams regardless of geographical locations. Shared access to files, real-time communication tools, and collaborative platforms enable employees to work together efficiently, enhancing productivity and fostering innovation.
- Remote Accessibility: With cloud computing, employees can access critical applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This feature enables remote work arrangements, providing flexibility for employees while ensuring business continuity.
- High Reliability and Availability: Cloud service providers typically offer robust uptime guarantees and redundant infrastructure to ensure high availability of services. This minimizes downtime risks and ensures that businesses can operate smoothly without interruptions.
- Automatic Software Updates: Cloud computing providers handle software updates automatically, ensuring that businesses have access to the latest features and security patches without requiring manual intervention or disruptions in operations.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud-based solutions often include built-in disaster recovery capabilities, such as data backups and replication across multiple locations. This helps organizations recover quickly from unexpected events and ensures business continuity even in challenging circumstances.
- Integration with Advanced Technologies: Cloud computing enables businesses to leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. By harnessing the computational power of the cloud, organizations can process large volumes of data and gain valuable insights to drive informed decision-making.
Overall, cloud computing solutions provide businesses with the agility, cost-effectiveness, security, and collaborative capabilities necessary to thrive in today’s digital landscape. By leveraging cloud-based services, organizations can focus on their core competencies while relying on reliable and scalable infrastructure to support their operations.
How secure is cloud computing?
Cloud computing security is a critical concern for businesses and individuals alike, and it’s important to understand the measures in place to protect data in the cloud. While no system can be completely immune to security risks, cloud computing providers employ robust security practices to safeguard data and infrastructure. Here are some key aspects that contribute to the security of cloud computing:
- Data Encryption: Cloud service providers typically use encryption techniques to protect data both at rest (stored) and in transit (being transmitted). This ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable without the encryption keys.
- Access Controls: Cloud providers implement strict access controls, including strong authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA). This helps prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive information.
- Physical Security: Cloud data centers are equipped with stringent physical security measures, including surveillance systems, access controls, and restricted entry points. These facilities are designed to prevent unauthorized physical access and protect against theft or damage.
- Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Cloud infrastructure often includes redundant systems distributed across multiple locations. This redundancy ensures that if one server or data center experiences an issue, services can continue uninterrupted from other locations. Regular backups and disaster recovery plans further enhance business continuity.
- Compliance Standards: Cloud providers adhere to industry-recognized compliance standards such as ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). These standards ensure that proper security controls are in place and regularly audited.
- Security Patching and Updates: Cloud providers take responsibility for applying security patches and updates to their infrastructure promptly. This minimizes vulnerabilities that could be exploited by potential attackers.
- Security Monitoring: Cloud environments are continuously monitored for suspicious activities or anomalies using advanced threat detection systems. This allows for early detection of potential threats or breaches, enabling swift action to mitigate any risks.
It is worth noting that while cloud providers have robust security measures in place, the responsibility for securing data in the cloud is a shared one. Users must also take precautions to protect their data, such as implementing strong passwords, regularly updating software, and utilizing encryption for sensitive information.
Ultimately, the security of cloud computing relies on a combination of strong security practices from cloud providers and responsible usage by individuals and businesses. By following best practices and choosing reputable cloud service providers, organizations can enjoy the benefits of cloud computing while maintaining a high level of security for their data.
What types of cloud computing solutions are available?
There are several types of cloud computing solutions available, each catering to different business needs and requirements. Here are some common types:
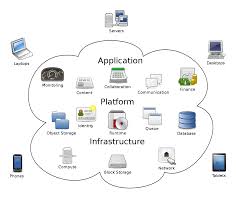
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities. With IaaS, businesses have the flexibility to manage and control their own operating systems, applications, and data while eliminating the need for physical infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. It provides a complete development environment with tools and services that enable developers to focus on building applications rather than worrying about hardware or software updates.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. With SaaS solutions, businesses can access ready-to-use applications without the need for installation or maintenance. Popular examples include customer relationship management (CRM) systems, project management tools, and email services.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing allows developers to build and run applications without managing servers or infrastructure resources directly. In this model, cloud providers handle tasks such as capacity provisioning and scaling automatically based on application demands. Developers only pay for the actual execution time of their code.
- Hybrid Cloud: A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments to provide greater flexibility and control over data placement. It allows businesses to leverage both on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services based on specific needs or regulatory requirements.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud refers to using multiple cloud service providers simultaneously to distribute workloads across different platforms or take advantage of specific features offered by each provider. This approach helps businesses avoid vendor lock-in while maximizing performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computation closer to where data is generated instead of relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure. It enables real-time processing and analysis of data at the edge of the network, reducing latency and improving performance for applications that require immediate responses.
These are just a few examples of cloud computing solutions available in the market. The choice of solution depends on business objectives, workload requirements, security considerations, and budgetary constraints. It’s essential to assess individual needs carefully and consult with experts to determine the most suitable cloud computing solution for a specific organization.
How much does cloud computing cost?
The cost of cloud computing can vary depending on several factors, including the specific cloud service provider, the type and amount of resources required, and the duration of usage. Cloud computing services typically follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users are charged based on their actual usage.
Cloud service providers offer various pricing options tailored to meet different business needs. Some common factors that can influence the cost of cloud computing include:
- Compute Resources: The cost of virtual machines or compute instances is usually calculated based on factors such as the number of instances, CPU power, memory capacity, and storage requirements.
- Storage: Cloud storage costs are typically determined by the amount of data stored and any additional features or redundancy options chosen (e.g., backup services).
- Data Transfer: Transferring data in and out of a cloud environment may incur additional charges. This includes both inbound data (uploading to the cloud) and outbound data (downloading from the cloud).
- Network Bandwidth: If your application or workload requires high network bandwidth for communication between components or users, there may be additional costs associated with increased data transfer rates.
- Additional Services: Cloud providers offer a wide range of additional services such as databases, machine learning tools, content delivery networks (CDNs), monitoring services, and more. These services often have their own pricing structures.
It’s important to note that while cloud computing offers flexibility and scalability benefits, costs can accumulate if resources are not managed efficiently. To optimize costs, businesses should regularly monitor their resource utilization, right-size their infrastructure to match demand, and take advantage of cost optimization tools provided by cloud service providers.
To get accurate pricing information for your specific requirements, it is recommended to consult with different cloud service providers directly or utilize their online pricing calculators that allow you to estimate costs based on your anticipated usage patterns.
How do I get started with a cloud computing solution?
Getting started with a cloud computing solution may seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, it can be a smooth and efficient process. Here are some steps to help you get started:
- Assess your needs: Begin by evaluating your business requirements and identifying the specific areas where cloud computing can add value. Determine what resources or applications you want to migrate to the cloud and define your goals for adopting cloud solutions.
- Choose a cloud service provider: Research and compare different cloud service providers based on factors such as reliability, security, scalability, pricing models, and customer support. Popular providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud.
- Select the right cloud model: Decide which type of cloud model suits your needs best – public, private, or hybrid cloud. Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers and offer scalability and cost-efficiency. Private clouds provide dedicated resources for a single organization, offering enhanced security and control. Hybrid clouds combine both public and private clouds to leverage the benefits of each.
- Plan your migration strategy: Develop a migration plan that outlines how you will transition your applications, data, and infrastructure to the cloud. Consider factors such as data transfer speeds, compatibility issues, dependencies between systems, and any necessary modifications or upgrades.
- Data security considerations: Ensure that you have robust security measures in place to protect sensitive data in the cloud environment. Implement strong access controls, encryption protocols, regular backups, and disaster recovery plans to safeguard your information.
- Train your team: Provide training and support for your employees to familiarize them with the new cloud-based tools and workflows they will be using. This will help ensure a smooth transition and maximize productivity from day one.
- Start small: Begin by migrating non-critical applications or workloads to the cloud first before moving mission-critical systems or sensitive data. This allows you to gain experience and confidence in the cloud environment while minimizing potential risks.
- Monitor and optimize: Continuously monitor your cloud usage, performance, and costs. Take advantage of the scalability and flexibility offered by cloud computing to optimize your resources and adjust as needed.
- Stay updated: Keep abreast of the latest developments in cloud computing technologies and services. Regularly review your cloud strategy to ensure it aligns with your evolving business needs and take advantage of new features or offerings that may benefit your organization.
Remember, it’s always a good idea to consult with experts or seek guidance from a trusted cloud service provider to help you navigate the process smoothly and make informed decisions.
What are the risks associated with using a cloud computing solution?
While cloud computing solutions offer numerous benefits, it is important for businesses to be aware of the potential risks and challenges associated with their adoption. Understanding these risks can help organizations make informed decisions and implement effective risk mitigation strategies. Here are some common risks associated with using a cloud computing solution:
- Data Security: Storing data in the cloud means relying on the security measures implemented by the cloud service provider. While reputable providers invest heavily in security, there is always a risk of data breaches or unauthorized access. It is crucial for businesses to carefully evaluate the security practices and certifications of their chosen cloud provider and ensure proper encryption, access controls, and data backup mechanisms are in place.
- Data Privacy: When data is stored in the cloud, it may be subject to different privacy laws and regulations depending on the jurisdiction where the cloud provider operates. Businesses must understand where their data will be stored, how it will be protected, and whether it complies with relevant privacy regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
- Service Reliability: Cloud service providers strive to provide high availability and uptime; however, occasional service disruptions or outages can occur due to various factors such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. Organizations should assess the reliability track record of their chosen provider and consider implementing backup plans or redundancies to minimize potential downtime.
- Vendor Lock-In: Migrating applications or data to a specific cloud provider’s environment may result in vendor lock-in. This means that switching to another provider or bringing services back in-house can be complex and costly. Businesses should carefully evaluate contract terms, interoperability options, and consider strategies for maintaining flexibility and portability of their data.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different industries have specific regulatory requirements that govern how sensitive information should be handled and stored. Organizations using cloud computing solutions must ensure that their chosen provider complies with relevant industry-specific regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for payment card data.
- Limited Control: With cloud computing, organizations rely on the cloud service provider for managing and maintaining the underlying infrastructure. This can result in limited control over certain aspects of the environment, such as software updates or hardware upgrades. Businesses should clearly understand their responsibilities and limitations within the cloud provider’s shared responsibility model.
To mitigate these risks, businesses can implement several strategies, including conducting thorough due diligence when selecting a cloud provider, implementing strong access controls and encryption mechanisms, regularly monitoring and auditing their cloud environment, and having robust backup and disaster recovery plans in place.
By understanding these risks and taking appropriate measures to address them, businesses can confidently harness the benefits of cloud computing while safeguarding their data and operations.
Are there any restrictions or limitations to using a cloud computing solution?
While cloud computing solutions offer numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of certain restrictions and limitations that organizations may encounter. Here are a few considerations:
- Internet Dependency: Cloud computing heavily relies on a stable and reliable internet connection. If your internet connection experiences disruptions or outages, it can impact your ability to access cloud services and data. It is crucial to have backup plans in place to mitigate the impact of potential connectivity issues.
- Data Security Concerns: While cloud service providers implement robust security measures, some organizations may have concerns about storing sensitive data on external servers. It is essential to thoroughly evaluate the security protocols and certifications of your chosen cloud provider to ensure compliance with industry regulations and safeguard sensitive information.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Certain industries, such as healthcare or finance, are subject to stringent compliance regulations regarding data privacy and protection. Before adopting a cloud computing solution, organizations must ensure that their chosen provider adheres to relevant compliance standards.
- Vendor Lock-In: When moving critical systems and data to the cloud, organizations may become dependent on a specific cloud service provider’s infrastructure and APIs. Migrating away from one provider to another can be challenging and time-consuming, potentially leading to vendor lock-in. Organizations should consider the long-term implications of their choice of cloud provider.
- Downtime Risks: Although reputable cloud providers strive for high availability, occasional downtime can still occur due to maintenance or unforeseen technical issues. It is crucial for businesses to understand their provider’s service level agreements (SLAs) regarding uptime guarantees, support response times, and compensation policies in case of disruptions.
- Data Transfer Speeds: Uploading large amounts of data or performing frequent backups/restorations over the internet can be time-consuming due to limited bandwidth capacities. Organizations should consider the initial data transfer process when migrating existing systems or large datasets into the cloud.
- Cost Management: While cloud computing can offer cost savings, it’s important to carefully manage usage and monitor costs. Organizations should regularly assess their resource utilization, optimize configurations, and consider reserved instances or pricing plans that align with their specific needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
By understanding these restrictions and limitations, businesses can make informed decisions about adopting cloud computing solutions and develop strategies to mitigate potential challenges. It is advisable to conduct a thorough analysis of your organization’s requirements and consult with cloud experts or consultants to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of cloud computing while addressing any limitations.