Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Solutions: Streamlining Business Operations for Success
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations need to stay ahead of the curve to thrive. One key aspect of achieving operational efficiency and success lies in adopting robust and comprehensive Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions. ERP systems have revolutionized the way businesses operate by integrating various core functions into a unified platform, enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and improving decision-making processes.
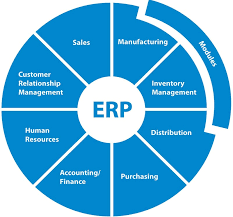
ERP solutions provide a centralized database that consolidates information from different departments within an organization. This integration enables seamless communication and collaboration across various functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management. By having all critical data in one place, businesses can streamline their operations and eliminate redundant processes.
One of the primary benefits of implementing ERP solutions is the automation of routine tasks. Manual data entry, complex spreadsheets, and multiple software applications can be time-consuming and prone to errors. With ERP systems in place, businesses can automate these processes, saving time and ensuring accuracy. This automation not only increases operational efficiency but also frees up valuable resources that can be redirected towards more strategic initiatives.
Furthermore, ERP solutions provide real-time visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs), enabling managers to make informed decisions based on accurate data. With access to up-to-date information on inventory levels, sales figures, production schedules, or financial reports at their fingertips, executives can react swiftly to market changes or identify areas for improvement. This data-driven decision-making approach empowers organizations to stay agile in an ever-evolving business environment.
Another significant advantage of ERP systems is improved collaboration among teams. By breaking down silos between departments and fostering cross-functional communication, employees can work together seamlessly towards common goals. For example, sales teams can access real-time inventory data to provide accurate delivery timelines to customers while procurement teams can align purchasing decisions with demand forecasts generated by the system. This collaboration not only enhances productivity but also enhances customer satisfaction and drives business growth.
Moreover, ERP solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt to changing market dynamics and growth opportunities. As organizations expand their operations or diversify into new markets, ERP systems can easily accommodate these changes. With a modular structure, businesses can add or remove functionalities as needed, ensuring that the ERP solution aligns with their evolving requirements.
Security is another critical aspect of ERP solutions. With sensitive data stored in a centralized system, robust security measures are implemented to protect against unauthorized access or data breaches. Regular backups and disaster recovery plans further safeguard critical business information, providing peace of mind to organizations and their stakeholders.
In conclusion, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions have become indispensable tools for modern businesses aiming to optimize their operations and achieve sustainable growth. By integrating various functions into a single platform, ERP systems streamline processes, enhance collaboration, improve decision-making capabilities, and provide scalability for future expansion. In today’s competitive landscape, investing in an ERP solution is a strategic move that can give businesses a significant edge over their competitors.
Frequently Asked Questions about Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Solutions
- What is enterprise resource planning solutions?
- What is an example of an ERP system?
- What is ERP system and how it works?
- What are the 5 components of ERP?
What is enterprise resource planning solutions?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions are software systems designed to integrate and streamline various core business functions within an organization. These functions typically include finance, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management. ERP solutions provide a centralized database that consolidates data from different departments, allowing for efficient communication and collaboration across the organization.
The primary goal of ERP solutions is to enhance operational efficiency by automating routine tasks and eliminating redundant processes. By having a unified platform for managing critical business functions, organizations can optimize resource allocation, improve productivity, reduce costs, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
ERP solutions offer a range of features and modules that cater to specific business needs. For example:
- Finance and Accounting: ERP systems provide tools for managing financial transactions, budgeting, cash flow management, accounts payable/receivable, general ledger, tax compliance, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources: ERP solutions offer modules for managing employee data, payroll processing, benefits administration, attendance tracking, performance management, training programs, and recruitment processes.
- Supply Chain Management: ERP systems enable organizations to manage their entire supply chain efficiently. This includes procurement of raw materials or goods from suppliers, inventory management, order processing and fulfillment, logistics planning and tracking, demand forecasting analysis.
- Manufacturing: ERP solutions help optimize manufacturing processes by providing tools for production planning and scheduling, materials requirement planning (MRP), shop floor control monitoring (including work orders and routing), quality control management.
- Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP systems integrate sales processes with customer relationship management functionalities. This includes managing leads/opportunities tracking in the sales pipeline; customer contact information; order management; after-sales support; marketing campaigns tracking.
- Reporting and Analytics: ERP solutions offer robust reporting capabilities with built-in analytics tools that allow organizations to generate customized reports on key performance indicators (KPIs) across various departments. These reports help in monitoring business performance, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions.
ERP solutions can be implemented on-premises or hosted in the cloud, depending on the organization’s preferences and requirements. They can be customized to suit specific industry needs, ensuring that businesses have a solution tailored to their unique operations.
Overall, ERP solutions serve as a comprehensive platform that integrates and optimizes various aspects of a business’s operations. By centralizing data and automating processes, ERP systems enable organizations to improve efficiency, enhance collaboration, make informed decisions, and ultimately achieve sustainable growth.
What is an example of an ERP system?
One example of an ERP system is SAP ERP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing). SAP ERP is a widely-used and highly comprehensive solution that helps businesses manage their core operations effectively. It integrates various functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management into one unified platform.
SAP ERP offers a range of modules that can be tailored to meet specific business needs. For example, the financial module enables organizations to manage accounting processes, financial reporting, budgeting, and cash flow management. The human resources module assists in managing employee data, payroll processing, recruitment, training, and performance evaluation.
The supply chain management module helps optimize procurement processes, inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics planning. The manufacturing module facilitates production planning and control, shop floor operations monitoring, quality management, and product lifecycle management.
Additionally, the sales and customer relationship management modules provide tools for managing sales processes from lead generation to order fulfillment. They also enable businesses to track customer interactions and enhance customer satisfaction through effective relationship management.
SAP ERP’s strength lies in its ability to centralize data from different departments into one database. This integration allows for real-time visibility across the organization and enables seamless communication between various functions. With extensive reporting capabilities and analytics tools provided by SAP ERP, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations for better decision-making.
It’s worth noting that while SAP ERP is a prominent example of an ERP system used by many large enterprises worldwide, there are other well-known ERP solutions available in the market as well. These include Oracle NetSuite ERP Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central/Finance & Operations (formerly known as Dynamics AX), Infor CloudSuite Industrial (formerly known as SyteLine), and many more. Each of these systems offers its own unique features and benefits tailored to meet specific industry requirements.
What is ERP system and how it works?
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive software solution that integrates and manages various core business functions within an organization. It serves as a central repository of data, providing real-time information and facilitating seamless communication across departments.
At its core, an ERP system works by consolidating data from different departments, such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management. This integration allows for efficient data sharing and eliminates the need for separate software applications or manual processes.
The functionality of an ERP system can vary depending on the specific needs of an organization. However, most ERP systems typically include modules or components that address key business areas. Some common modules include:
- Finance and Accounting: This module manages financial transactions, tracks expenses, generates financial reports, and facilitates budgeting and forecasting.
- Human Resources: The HR module handles employee information, payroll processing, benefits administration, performance management, recruitment, training, and employee self-service functionalities.
- Supply Chain Management: This module oversees inventory management, procurement processes, order processing and fulfillment, demand forecasting, supplier relationship management (SRM), and logistics.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing module streamlines production planning and scheduling, materials requirement planning (MRP), shop floor control activities like work orders tracking and routing optimization.
- Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This module manages sales processes including lead generation to order fulfillment while also tracking customer interactions to enhance customer service.
ERP systems function by capturing data from various sources within the organization in real-time or near-real-time. This data is then stored in a centralized database accessible to authorized users across different departments. By having a single source of truth for critical information like inventory levels or financial transactions, decision-makers can access accurate data to make informed decisions promptly.
Additionally, ERP systems often offer reporting tools that allow users to generate customized reports based on specific criteria or key performance indicators (KPIs). These reports provide insights into the organization’s performance, helping management identify trends, areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions.
The implementation of an ERP system involves several steps, including planning, system configuration, data migration, customization, training, and ongoing support. The system can be hosted on-premises or in the cloud, depending on the organization’s preferences and requirements.
Overall, an ERP system acts as a centralized platform that integrates various functions and data within an organization. It streamlines processes, enhances collaboration, improves decision-making capabilities, and provides a holistic view of the organization’s operations for efficient management.
What are the 5 components of ERP?
The five components of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) are:
- Hardware: This component refers to the physical infrastructure required to support the ERP system, including servers, computers, networking devices, and storage devices. The hardware should be capable of handling the processing power and storage requirements of the ERP software.
- Software: The software component comprises the ERP application itself. It includes modules or functionalities for different areas of business operations such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management. The software is designed to integrate these functions into a unified system.
- Data: Data forms a crucial component of an ERP system. It includes all the information required for business operations, such as customer data, product information, financial records, inventory levels, employee details, and more. The data is stored in a centralized database and is accessible across various modules within the ERP system.
- Procedures: Procedures encompass the set of rules and guidelines that govern how users interact with the ERP system. This includes defining workflows, documenting standard operating procedures (SOPs), establishing data entry protocols, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Well-defined procedures help ensure consistency and accuracy in data entry and streamline business processes.
- People: People are an essential component of any ERP implementation. This refers to the individuals who use and manage the ERP system on a daily basis – including end-users who input data or perform tasks within specific modules as well as IT personnel responsible for maintaining and supporting the system. Proper training is crucial to ensure that users understand how to effectively utilize the ERP software for their respective roles.
These five components work together to create an integrated and efficient ERP system that enables organizations to streamline operations, enhance collaboration between departments, improve decision-making processes based on accurate data insights, and drive overall business success.